
Online Journals
Energy Analysis, Building Energy Index and Energy Management Strategies for Fast-Food Restaurants in Malaysia
Commercial buildings in Malaysia contribute to 35% of the total electricity demand. During the recent COVID-19 pandemic, the global economy faced a challenging situation that forced many businesses to shut down. However, fast-food restaurants with drive-through features managed to get through this pandemic phase without much effect from the economic impact. Since COVID-19, the operational guidelines have changed for restaurants. However, from an energy perspective, fast–food restaurants are high energy consumers in the retail sector. This paper analyses the load profile of fast-food restaurants and the potential strategies that can be adopted in a free-standing fast-food restaurant. From analysis, it is calculated that a total of RM 97,365.9 of utility savings can be obtained in a year. A total of 91,392.1 kg CO2, 881.8 kg SO2 and 385.5 kg CO pollutant emissions can be reduced. The BEI for the restaurant was reduced to 856.4 kWh/m2/year. By converting to energy-saving strategies, the return on investment was 27.3% and 3.7 years, which is a very short period of time and is attractive for businesses of this nature.
For full paper, please visit https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013515

Selection Criteria of Building Material for Optimising Maintainability
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the principles and criteria that govern selection of building materials in achieving building maintainability. The methodological approach used findings generated from extant literature to establish a set of principles and respective criteria for selecting building materials in respect of their influence in achieving building maintainability in post construction (occupancy) period. Further, a modified Delphi method, comprised of a series of questionnaire surveys among the sample of experts drawn from relevant fields including architecture, maintenance, structural engineering and so on, was conducted and the data obtained from which were used to reveal the relationships between the criteria and building maintainability. This paper presents findings on material selection criteria and their relationship to building maintainability. A structural relationship model showing the relationship between maintainable building material selection criteria – attributed to respective principles – and building maintainability is presented. Principles like “Technical Performance of Materials”, “Documentation and Details”, “Mechanical Properties of Materials”, “Chemical Properties of Materials”, “Material Economy” and “Social Benefit” have been identified as the most significant ones for optimising building maintainability in general. It is advocated that these sets of criteria attributed to respective principles need to be formally used in selecting materials for achieving building maintainability. This research is context-bound exclusively to the Malaysian construction industry. Its wider implications need further investigations. This study contributes to the building industry and maintainability research in at least one significant aspect that it widens understanding on maintainability criteria to be considered in selecting maintenance friendly materials and their influence in partially achieving post construction maintainability. The model presented in this paper would enable decision makers to ascertain, during the design phase, what maintainability principles and criteria would require more attention than others to achieve building maintainability.

For complete paper, please visit https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.108
Illuminance Uniformity Using Public Works Department (PWD) Standard Design for Public School Classroom Design in Malaysia
Illuminance or lighting level is an important factor in ensuring conducive environment for studying in Malaysian public school. The design lighting level is based on the existing Public Work Department standard design which will help to evaluate on the daylight distribution in public school. However, despite the present of the existence PWD standard design, research still had to be carried out to determine, review, and identify the level of deficiency and improvement needed to be taken upon the PWD standard design to evaluate on the daylight distribution levels. This is because based on the current research related to illuminance value showed that there were some poorly lit spots within the classroom which are uneven that will affect the students’ performance. Based on this research study, analysis is carried out based on physical data and IES simulation software which enable to test the classroom under different sky conditions, orientations and time frame which allows the classroom to receive optimum daylight value.
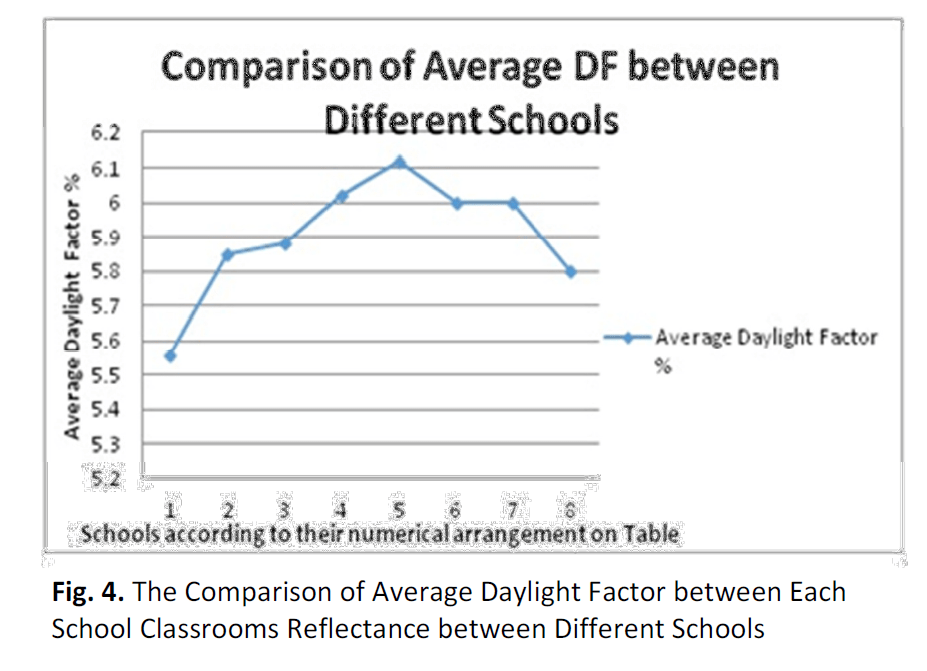
For full version of paper, please visit http://www.akademiabaru.com/doc/ARFMTSV52_N2_P205_214.pdf
Perception of Lecturers and Students Regarding the Illuminance in the Lecture Theatres and Tutorial Rooms: Case Study in Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (UTAR)
Even though artificial lighting is widely used nowadays, it has several negative impacts on human health. Therefore, this paper reported research that comparing the illuminance level in the learning environment in UTAR and recognizing the users’ insights on the illuminance level. Lux meter and questionnaires were used for data collection. Questionnaires were administered to 312 respondents. The results show that the illuminance level in some of the tutorial rooms is too bright and left on even when the rooms are empty. From the descriptive analysis, it is found that almost all the respondents are satisfied with the illuminance level in both research venues. Based on the t-test, it is found the significance for pair 1 and pair 2 is greater than 0.05. Hence, there is no similarity between both research venues. Pair 1 is about the lighting condition preferred by the respondents, while pair 2 is about the condition in both research venues which includes the existence of glaring vision, headache, eye tiredness, and conditions that affect student performance. This paper concludes by suggesting that individual switches be provided for each of the bulbs.
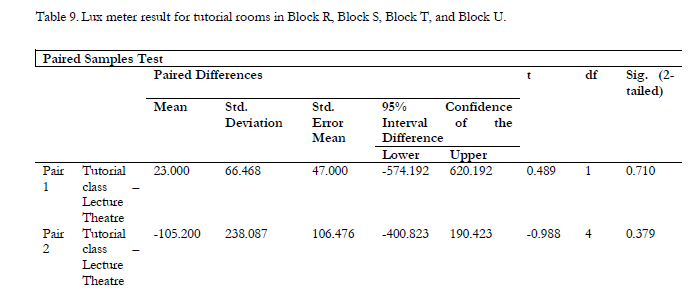
Please visit https://doi.org/10.4186/ej.2021.25.7.83 for full paper
A Comparison of Criteria Between GreenRE and International Green Rating Tools in Green Construction Projects: A Review
The global construction sector is moving towards sustainable development by implementation of green rating tool to monitor the overall process of construction activities. Existence of green rating tool during the construction and operation period will significantly reduce the emission of carbon contributed from construction industry. Besides that, monitoring process by the green rating tool for the newly constructed green building also able to promote the usage of energy saving related technologies during the operation period of the constructed green building by the end users. However, despite the advent made for the establishment of green rating tools globally, not much had been done to determine, review, compare and identify the differences and similarities between green rating tools. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to compare the GreenRE rating tool to other international green rating tools. Three international green rating tools, Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Methodology (BREEAM) (UK), Green Star (Australia) and Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) (US) will be compared to Malaysian rating tool, GreenRE. The findings from this study through the comparison of international and Malaysian rating tool will reveal the rating systems available in terms of their similarities and differences which will help to improve the effectiveness of green building assessment methods in Malaysia towards achieving goals of green development in Malaysian construction industry. Furthermore, research findings in this study will act as a steppingstone to guide the establisher and assessors of GreenRE to improve the green rating tool system towards perfection in Malaysian green construction industry.
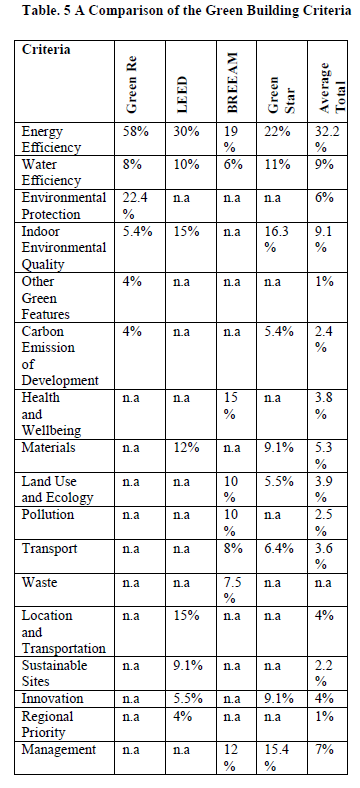
To check the full paper, please visit,
https://www.ijitee.org/wp-content/uploads/papers/v8i5s/ES3432018319.pdf
Green Homes Development in Malaysia: A Review on Energy Perspective
Nowadays, Malaysia already has a green building index to make sure that everyone in
the construction industry will take sustainable development critically. This study attempted to examine the existing literature of energy efficiency and alternative resources that has been produced in developed countries. By reviewing the existing literature found that the energy efficiency more focus on the designs of the houses and encouragement from government in practices of green energy in housing development. For future studies, it is recommended more studies involving the other stakeholders in the industry should be done. These are the housing developers, authorities, suppliers and contractors. Comparison of these industry contributors may provide a better understanding of how energy practices can enhance house buyers’ requirements of green homes in Malaysia.
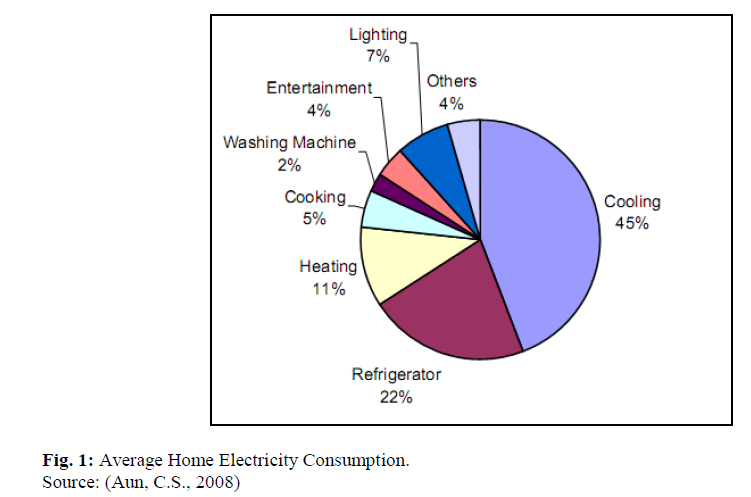
Please visit http://www.ajbasweb.com/old/ajbas/2015/April/340-344.pdf for full paper.
Analysis on Comparison of Factors Influencing the Success of Sustainable Construction
Malaysia started to implement several national policies related to sustainable development since 1980’s such as National Energy Policy (1980), National Depletion Policy (1980), Four Fuel Diversification Policy (1981) and Fifth Fuel Policy (2000). Subsequently, sustainable construction already started to evolve since the beginning of Eight Malaysia Plan by integration of social, economic and environment. But sustainable development in Malaysia is still in initial stage as more research and development in terms of facilities and renewable energy resources are needed. Based on the previous researchers, there are six factors which influenced the development of sustainable construction. The six factors are factor related to project, factor related to project manager, factors related to project team, factor related to material and equipment, factors related to client and factors related external. Furthermore, identification of success factors will eventually leads to development of theoretical framework of success factors of sustainable construction. The findings from this study through the identification and comparison of success factors will reveal the weakness and advantages of existing factors and help to improve the success factors of theoretical framework. This research study uses survey method or questionnaire for data collection process. There are total of 120 questionnaires distributed to respondents which consists of contractors in location around Peninsular Malaysia. The research data have been analysed with factor analysis method using Smart PLS.
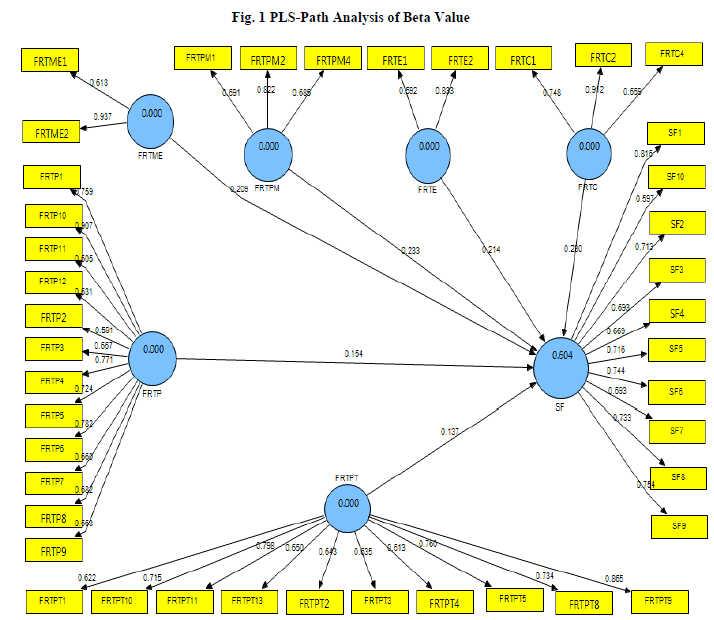
For complete paper, please visit
https://www.ijitee.org/wp content/uploads/papers/v8i5s/ES3433018319.pdf
What is Stopping the Adoption of Sustainable Residential Buildings in Malaysia?
Researchers and the government have advocated for the delivery of sustainable building projects in Malaysia; however, the rate of demand and supply of the sustainable residential buildings has been low and the increase is slow. This research aims to examine the barriers towards the adoption of a sustainable residential building. This research conducted a cross-sectional survey using a questionnaire comprising 19 barriers to adoption of sustainable residential buildings administered on 110 professionals in the building industry. The research found that 89% of the responding housing professionals observed that there are barriers obstructing the adoption of sustainable residential buildings. The research found that a lack of experience on sustainable building projects by the industry, maintenance problems, lack of technology for the delivery of sustainable building projects, lack of competent labour in sustainable buildings, and the high capital cost of sustainable residential buildings compared with the conventional buildings are the five main barriers stopping the adoption of sustainable buildings in Malaysia. Based on the findings, it infers that the delivery of sustainable housing depends on the technological advancements, policies, competencies, awareness, homebuyers’ experience, and costs. The research concludes by presenting a cycle of barriers for the rapid adoption of sustainable buildings. The findings provide feedback and feedforward information to the policymakers, design and construction teams, and manufacturers.
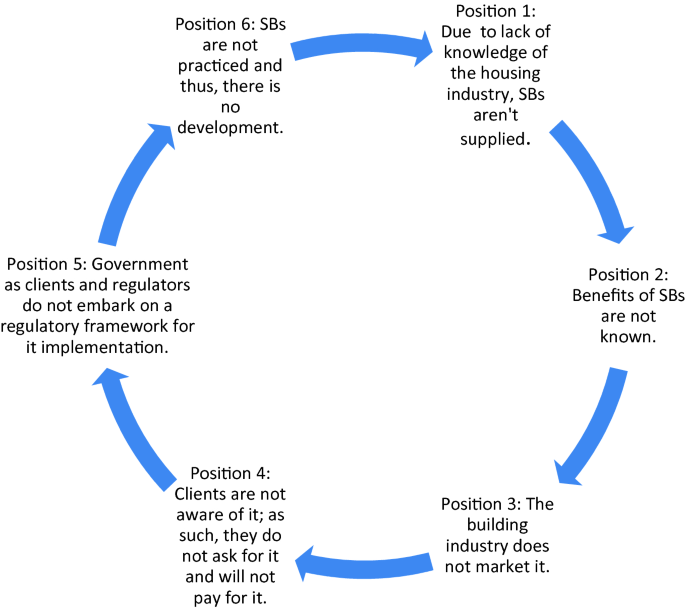
For complete paper, please visit https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-24650-1_10
A Case Study of an Office Building to Identify Energy Consumption and Carbon Management Solutions Using Physical Data and Simulation Software
To measure the level of energy performance of a building, there are several categories of energy consumption to be calculated such as oil, natural gas and electricity. In order to significantly minimise the Greenhouse gas emission in an office, it is important to tap into the positive progress of energy efficiency of equipment which contributes to total energy performance of a building. Consequently, to enable accurate building energy consumption of a building, energy modelling method is applied to identify total consumption and cost of energy usage with effects of carbon emission. Hence, this will help to reduce the costing of energy inside building with differences of efficiency options. Therefore, this paper aims to analyse an office building in terms of the level of energy consumption and carbon emission as a case study. The first objective is to identify the amount of energy consumption and carbon emission inside the building using the simulation software. Secondly, to identify the differences between the data recorded through simulation software and physical data. Finally, to identify solutions to decrease the carbon emission by applying measures towards reducing energy consumption inside the building.

To check the full paper, please visit, https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/945/1/012049